Introduction
What does Scrum mean?
In Agile software development, a daily meeting in which each developer describes what they have been doing, what they plan to do next, and any impediments to progress.
Scrum is a management and control process that cuts through complexity to focus on building software that meets business needs.
Scrum meeting is conducted daily for 15 minutes, where members are asked main three questions; “What did you do since last meeting?”, “What will you do today?” and “What impediments do you have in your way?”.
Purpose of Scrum in Agile Development
To support agile terms in collaborative and coordinating their work with other terms.
Here in Vorlik, we have introduced Scrum Management with Project Module, where we have tried to fulfill all the functionalities of Agile Software Development.
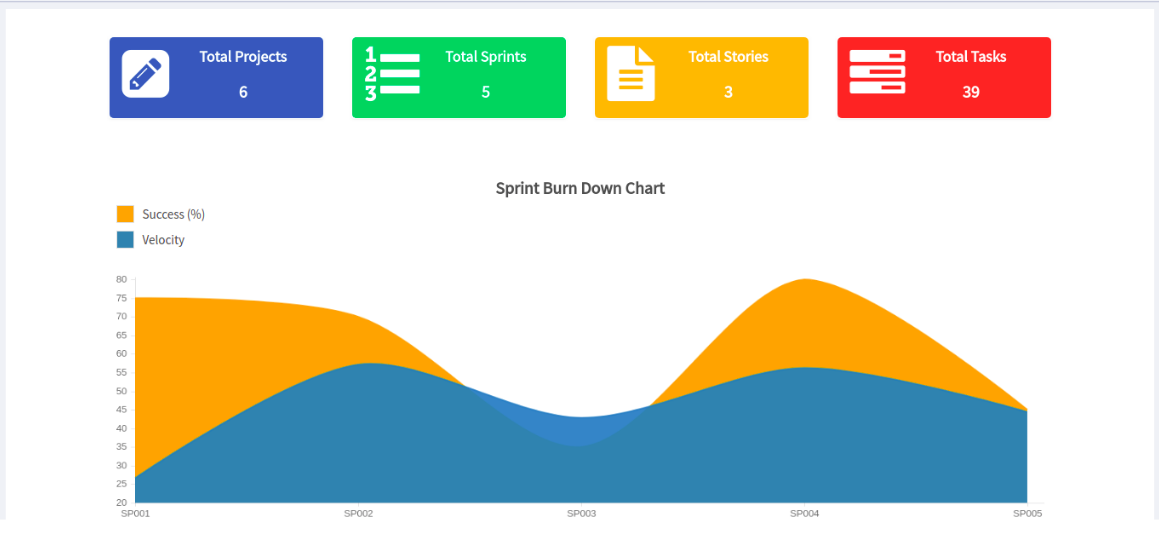
Sprint Dashboard
You will get statistical counts of Sprints, Tasks, Stories, Project for all at once.
Dashboard gives you the idea of scrum where you can see a Burndown chart, which shows number of sprints with its Estimated Velocity and Actual Velocity.
Project Team
Project Team is a group of experts in different technologies with different skills, who are liable for project development.
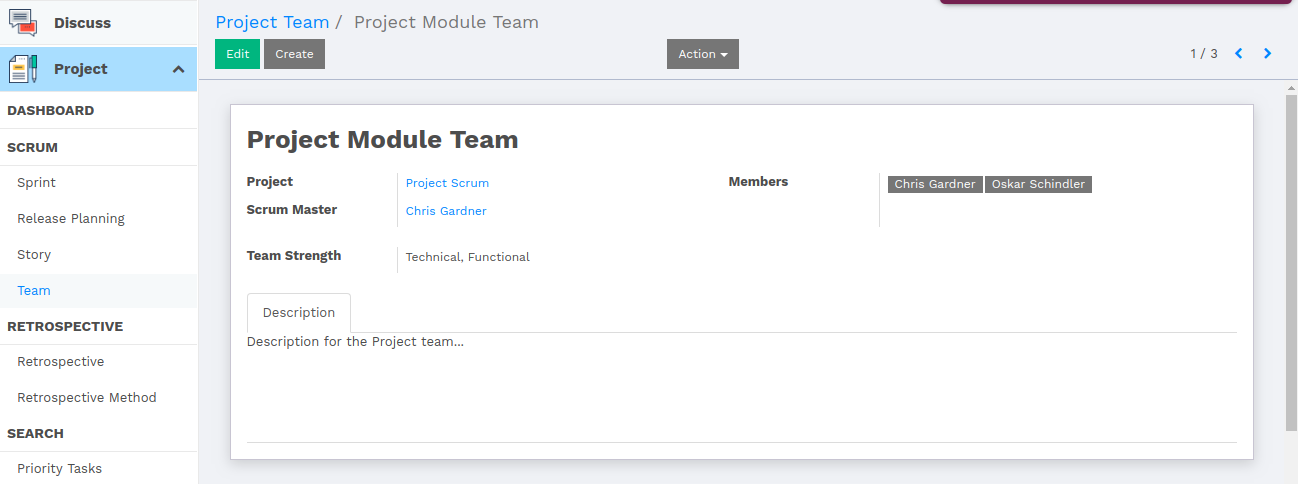
Attributes of the project team are as follows:
- Scrum Master : A scrum master is a facilitator for an agile development team. The scrum master manages the process of how information is exchanged.
- Members : Members are Project developers who are expert in particular field or technology.
- Project : The task or responsibility, the team is allocated for.
- Team Strength : Team strength describes the expertise level of the team, which describes team member with their skills.
- Description : Description describes the overview of the project, which gives idea to the members of the project.
Sprint
In product development, a sprint is a set of period of time during which specific work has to be completed and made ready for review.
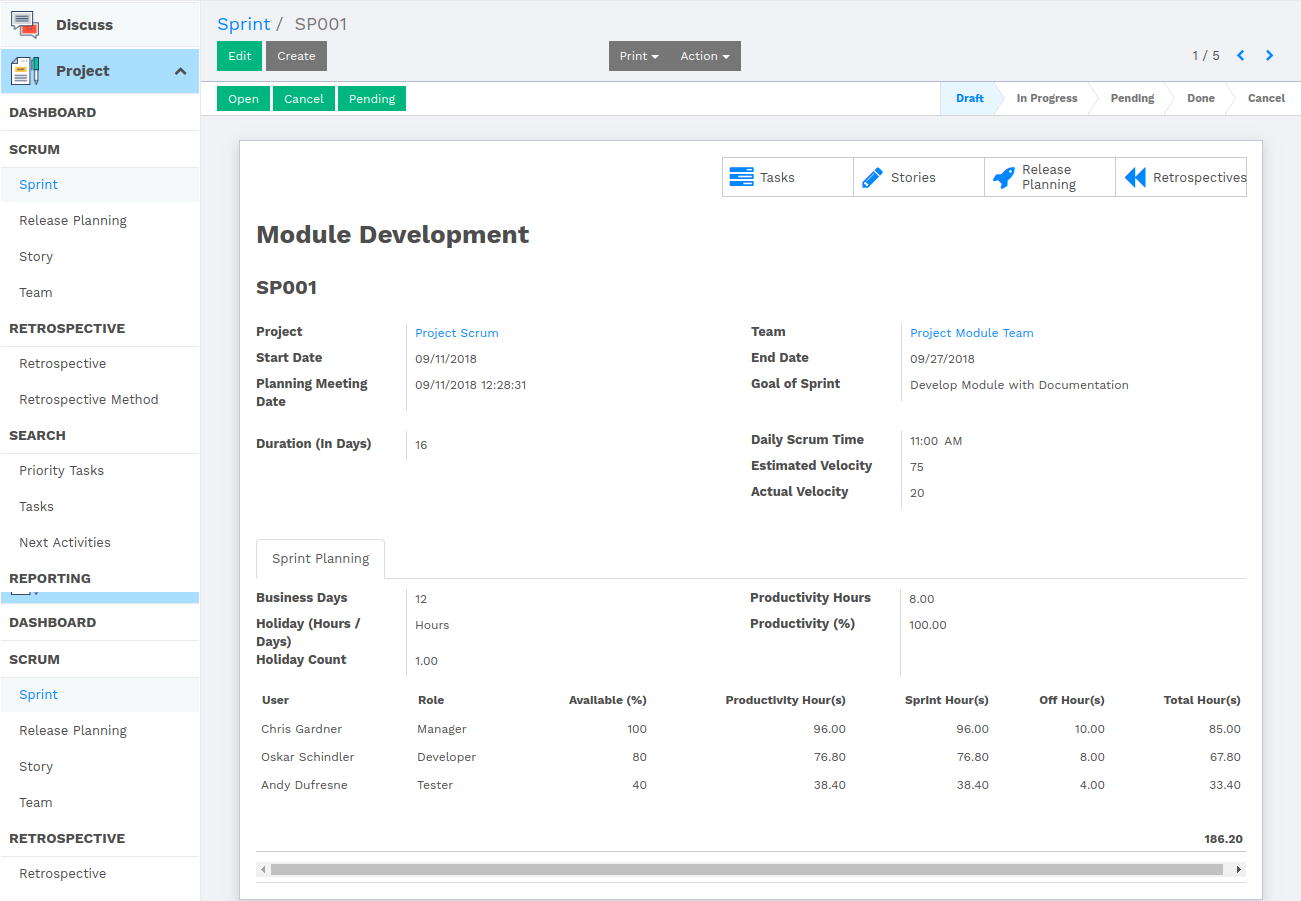
Task is compartmentalized between few parts which are covered by a single sprint.
Sprint contains attributes which are as follows:
- Project - The associated project.
- Team - The team, working on sprint.
- Duration - Duration of the sprint.
- Daily Scrum Time - The time when scrum meeting is to be conducted.
- Velocity - Velocity indicates the complexity of the sprint in points.
- Sprint Planning - This shows the productivity hours spent by each member of the project scrum
We have put smart buttons to the top right corner of the sprint, which shows Tasks, Stories, Release Plannings and Retrospectives according to the current sprint.
Velocity
Velocity is the measure of the amount of work a team can tackle during a single sprint and is the key metric in Scrum. Velocity is calculated in the end of the sprint by totalling the points of all fully completed tasks.
Velocity in the sprint is calculated by adding velocity of all the tasks related to the sprint.
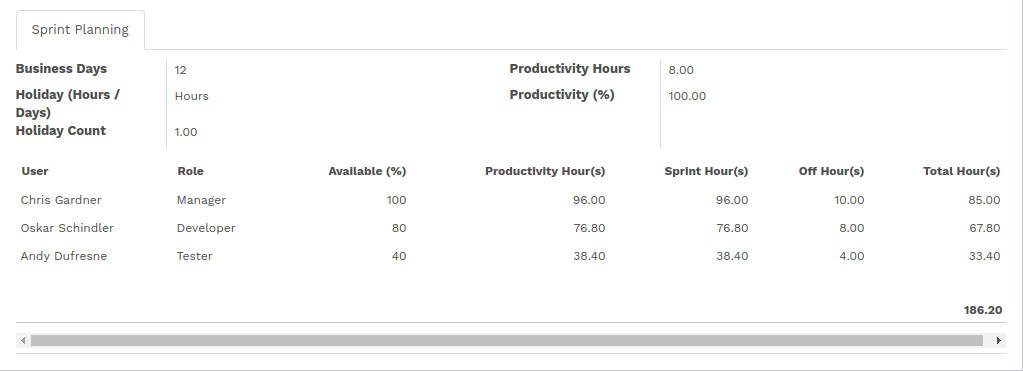
Sprint Planning
Here is a calculation of sprint planning, which shows Productivity time given to the sprint by each member of the team.
Productivity Hours Calculation for team member
- Available Percentage - Availability of particular team member in percentage
- Business Days - Start date of the sprint - End date of the sprint
Number of days - Number of working days of the week
Productivity Hours = [Available Percentage * Business Days * Number of days] / 100
Sprint Hours Calculation for team member
- Available Percentage - Availability of particular team member in percentage
- Business Days - start date of the sprint - end date of the sprint
Productivity Hours = Working hours / Total Hours
Sprint Hours = [Available Percentage * Business Days * Productivity Hours] / 100
Total Hours Calculation for team member
[Total Hours = Sprint hours - Holiday count(In Hours) - Off hours]
Project Story
Project Stories are one of the primary development artifact for scrum project team. A user story is a very high-level definition of a requirement, containing just enough information so that the developers can produce a reasonable estimate of the effort to implement it.

A story may contain multiple tasks, there may have a single story containing all the user requirements for Project tasks.
Attributes of Project Story are as follow:
- Sprint : The sprint which is associated to the project
- Priority : Priority of the story
- Owner : Owner of the story (Who wrote the story)
- Estimated Velocity/Actual Velocity : Velocity of the story
- Description : Description of the story
Velocity of the story is calculated by totalling the velocity of each task related to the current story.
Release Planning
A very high-level plan for multiple Sprints is created during the Release Planning. It is a guideline that reflects the expectations about which feature will be implemented and when they are completed. It also serves as a base to monitor progress within the project. Release can be intermediate deliveries done during the project or the final delivery at the end.
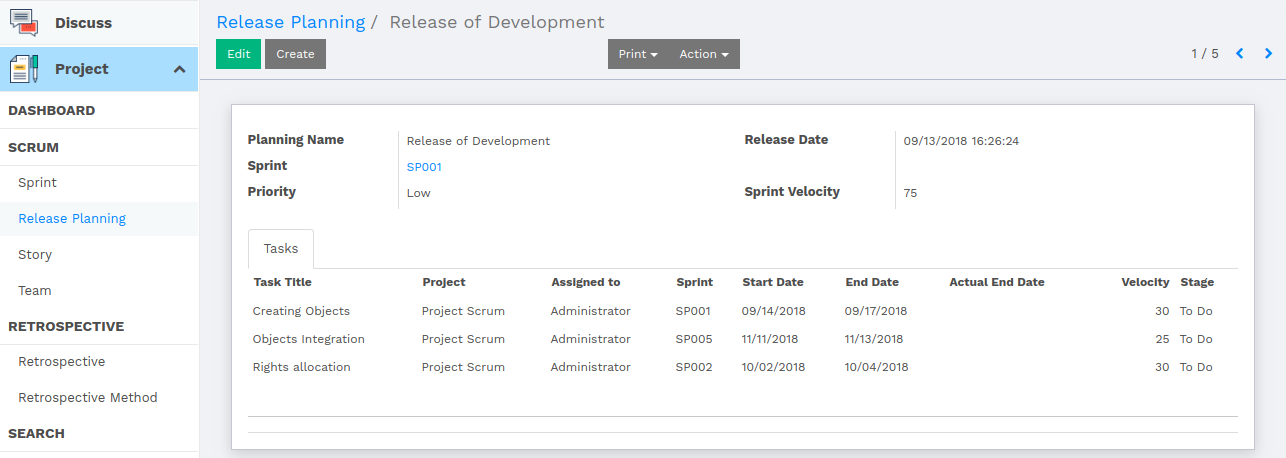
One sprint can have multiple release plannings according to the task divided into several subtasks. Whichever subtask is completed first, will be treated for releasing.
Attributes of Release Planning are as follows
- Sprint - Sprint associated to the release planning.
- Priority - How important the current release planning is, that is shown by priority.
- Release Date - Date of Releasing.
- Tasks - Number of tasks, which shows that how many of them are going to be released under the plan.
Retrospective
Retrospective is meeting that helds at the end of an iteration of development life cycle. During the retrospective, the team reflects on what happened in the and identifies actions for improvement going forward.

The sprint retrospective is meeting facilitated by the Scrum Master at which the team discusses sprint and determines what could be changed that might make the next sprint more productive. The sprint review looks at what the team is building, whereas the retrospective looks at how they are building it.
Attributes of Retrospective are as follow
- Sprint - The sprint which is going through the retrospective.
- Retrospective Method - Method, that is used for the retrospective process.
- Scrum Master - The one who held the process.
- Retrospective Lines - It has two fields, User and Message, where the current logged in user gives the review on the Sprint as per the process.