The cash basis taxes are due when the payment has been done and not at the validation of the invoice (as it is the case with standard taxes). Reporting your income and expenses to the administration based on the cash basis method is legal in some countries and under some conditions.
Example : You sell a product in the 1st quarter of your fiscal year and receive the payment the 2nd quarter of your fiscal year. Based on the cash basis method, the tax you have to pay to the administration is due for the 2nd quarter.
How to configure cash basis taxes ?
You first have to activate the setting in . You will be asked to define the Tax Cash Basis Journal.

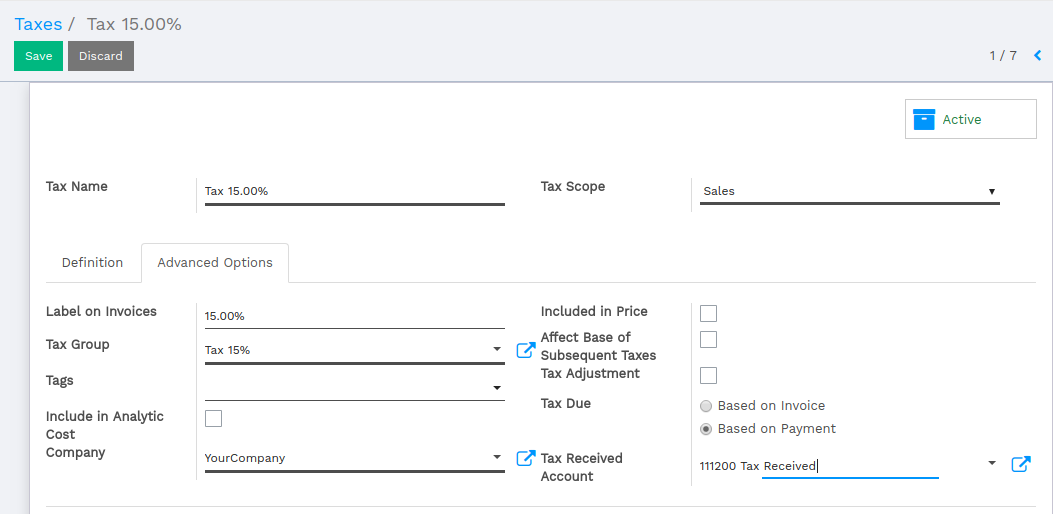
Once this is done, you can configure your taxes in . You can open a tax and in the Advanced Options tab you will see the radio button Tax Due. Now, select Based on payment. You will then have to define the Tax Received Account.
What is the impact of cash basis taxes in my accounting ?
Let’s take an example. You make a sale of $100 with a 15% cash basis tax. When you validate the customer invoice, the following entry is created in your accounting:
| Customer Invoices Journal | |
|---|---|
| Debit | Credit |
| Receivables $115 | |
| Tax Account $15 | |
| Income Account $100 |
A few days later, you receive the payment:
| Bank Journal | |
|---|---|
| Debit | Credit |
| Bank $115 | |
| Receivables $115 |
When you reconcile the invoice and the payment, this entry is generated:
| Tax Cash Basis Journal | |
|---|---|
| Debit | Credit |
| Tax Account $15 | |
| Tax Received Account $15 | |
| Income Account $100 | |
| Income Account $100 |
Tip
The two journal items created in the Income Account are neutral but they are needed to insure correct tax reports in Vorlik.